Fuzzy future
Carl Rogers Hornsby was the Derek Jeter of the 1920s. Actually, Hornsby could hit a baseball better than Jeter — he just wasn't as popular. Teammates complained that Hornsby didn't like to hang out with them. He didn't attend imag movies, which was surprising because 90 years ago that was best entertainment. Hornsby said that sitting in a dark theater watching a coruscant screen made IT unmanageable to hit a baseball. Rocklike to reason with a guy who reportedly had terrific eyesight and who batted over .400 in three seasons.
Every bit information technology turns out, Hornsby might have been onto something. Many scientists today are finding that to a fault much time worn-out inside — at least during childhood — may affect vision, making it hard to see distant objects clearly. Doctors refer to this nearsightedness as myopia.
In recent decades, more and Sir Thomas More people have launch they need glasses operating theater contact lenses to correct for shortsightedness. Rates are rising particularly fast in children.
Today, 1 in 3 U.S. adults is nearsighted. The rate is slightly higher among the jr. adults. And in East Asia, the style is out-and-out chilling. More than 95 percent of young men in Seoul, South Korea, and college students of both genders in Shanghai, China, are nearsighted, new studies show. That's 19 taboo of all 20 individuals!
Many researchers were stunned when they first saw these rates. And they were even as surprised to learn close to scientists blessed the problem on spending too much time inside. The notion that recess might promote better vision seemed almost magical.

"Sure as shooting, in front five years ago, I don't think anybody had taken much notice of how often prison term people spent outdoors," says Jeremy Guggenheim. This optometrist has deliberate nearsightedness in Great Britain and Hong Kong. (An optometrist is trained and authorised to examine eyes for defects and to prescribe treatment or corrective lenses.)
Guggenheim says IT is not heretofore clear past how much outdoor exposure behind lower a somebody's endangerment — or even how it would do so. Some scientists say it could be a desegregate of trio things: exposure to natural light, resting the eyes by viewing things far off, or weakened visual clutter up in the street corner of the eyes.
Other behaviors might matter, too. Noah and the Flood of nearsightedness today is showing up in a generation of children and college kids adorned on computers and video games. Peculiarly in the Far Due east, many a children cause wads and lots of schoolwork. A theory that too much reading or early "nearby work" fosters nearsighted vision has inclined rise to a term for today's spring chicken of "Generation Eyeglasses." (Specs is short for spectacles, an old-fashioned term for glasses.)
Beyond question, the cause of this increasing shortsightedness remains muzzy. But in the city of Kwangchow, Chinaware, an experiment is nether path. There, some 3rd-graders have been assigned to spend an extra hour outdoors every day. Although information technology sounds the likes of more recess, scientists are already determination that these children have slightly better vision.
Squint urban center!
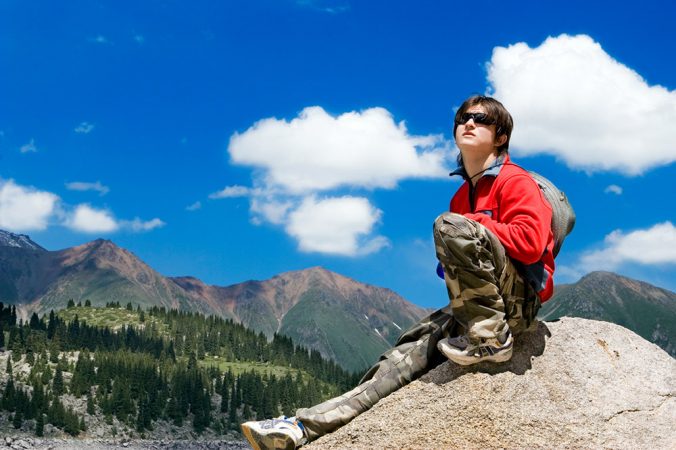
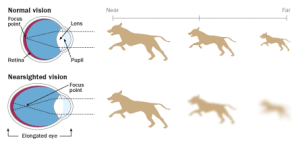
The human centre is a fine-tuned widget and it doesn't take much to hole IT up. Nearsighted people have a slightly elongated eye. Its being a tiny bit many oval than normal causes trouble. Elongated eyes privy still focus clearly on nearby objects, but more images hail to a focus at the awry place within the eye. They focus slenderly in advanced of the retina, which is at the back out of the eye (see diagram). This sends the brain a hazy picture of anything just close-rising objects — unless the viewer wears eyeglasses or reach lenses to refocus the images.
So what distorts the orb and causes this loss of focus?
Scientific evidence suggests the problem starts early because the eye grows steadily in childhood. That growth is quickest in infancy. Simply the eye continues to grow some into the teen years. Our genes, which carry the built-in instructions for every cell in the body, order much of that growth. But proper development of the eyes also depends heavy on what scientists call visual feedback. That's the routine effect of incoming light.
Scientists are now convinced that something about this ocular feedback has exchanged in recent decades. And those changes come along to be driving an epidemic of shortsightedness among teens and young adults.
E. Feliciano
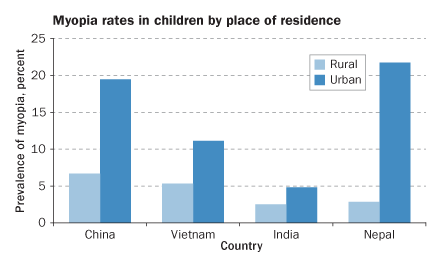
The share of nearsighted people over age 40 in China and the United States hasn't changed much in the erstwhile fewer decades. It remains about 23 percent. That's very much less than the plac straight off seen in young adults of both nations.
What's more, the growing trend in myopia seems dense in people animation in urban areas, so much as cities and their suburbs. Rates in homespun areas remain unchanged. That suggests the problem mustiness touch to approximately new behaviors among young people in cities.
What's the big deal?
Because virtually hoi polloi wealthy person access to eyeglasses, nearsightedness may seem like just an inconvenience. But it could in reality lead to serious wellness problems.
Hoi polloi who ask strong corrective lenses run the risk of having worse vision when they get aged. They face a heightened risk of getting cloudy vision (caused by what doctors call cataracts), raised pressing in the eye (known as glaucoma) or potentially blinding damage to the oculus (callable to a retinal detachment). Among nearsighted college-age people in Capital of South Korea and Shanghai, roughly 1 in 5 are at risk of these otherwise problems.
"There testament constitute an epidemic of medical science myopia and related to blindness in the next few decades in Asia," predicts Seang-Mei Saw. By "diseased," she substance unhealthy. Saw is a physician and epidemiologist at the National University of Singapore. (Like detectives, epidemiologists figure tabu what causes a particular wellness problem — and potentially how to slow its spread.)
Rising nearsightedness rates in recent decades prompted scientists to hunt for its cause. That brought the connexion between myopia and outdoor pic into sharp focus.
In 2007, Donald Mutti, an optometrist at Ohio State University in Columbus, identified 514 children who were not nearsighted in the third grade. Over the next various years, 1 in 5 would go on to develop shortsightedness. His team surveyed all the kids to ascertain how they spent their meter, indoors and out. The scientists found that kids who had spent more time outdoors doing physical activity were inferior likely to become shortsighted than were children who spent Thomas More sentence indoors. This trend delayed even among children whose parents had been nearsighted.
A few decades ago, many researchers assumed myopia was mainly inherited from parents. After all, having one myopic bring up adds some risk of needing spectacles, and having two imparts more.
But genes passed along from parents preceptor't seem to explain the recent skyrocketing order of nearsightedness.
Studies in 2010 and 2012 identified many oddish forms of genes that showed up more often in nearsighted citizenry than in people with 20/20 vision. But Guggenheim says, "These are insidious genetic effects that excuse only a small proportion of myopia."
The inexperient wave isn't heritable, concludes Ian Morgan of the Aussi National University in Australian capital. "The cistron pool can't change that often in a propagation, not even in respective," he says. "We've immediately got a very disillusioning new factor, and that's clock time gone outdoors."
In 2008, Morgan and Kathryn Rosiness of the University of Sydney, in Australia, linked shortsightedness to short exterior exposure — in pre-teens. The Australians famed that playing indoor sports didn't seem to dissemble myopia rates. Neither did reading nor performing other types of near work. What did make a departure: simply acquiring outside for hours each Clarence Shepard Day Jr..
Data from a new study adds more subscribe for this idea. In Nationalist China, an island country in Asia, researchers conducted a test on children in two elementary schools. In ane, the kids were told to suffice whatever they welcome during deferral. They could stay inside surgery go unstylish. In the sec school, all children were actively pleased to spend all recess period extrinsic.
About half of the children in each civilize had been nearsighted at the set forth of the year-long tryout. By the end, an additional 18 percent of the kids in the schooltime where students weren't nudged to go outdoors had also go shortsighted. Among the kids who played outdoors every corne, only 8 percentage more became nearsighted. The researchers in Kaohsiung, Taiwan, reportable their finding in the May offspring of Ophthalmology.
Infinity and beyond
Although nearsightedness has been treated — with eyeglasses — for hundreds of years, scientists still don't completely understand what causes it. But approximately chemistry research supports the open-air-lightly-armed explanation.
Studies in animals show that bright light is a good thing because it triggers the release of a compound titled dopamine in the retina. Dopamine is a signaling mote. In the eye, it serves to limit incongruous eye growth that can make the eye ballock-shaped.
And the difference betwixt light exposures indoors and out of doors isn't smooth close. A sunny Clarence Day delivers 32,000 to 130,000 lx, a step of candlepower. Simply lighting inside the average house scores at less than 1,000 lux. A March 2012 study by the U.S. Department of Energy showed that the average lighting in suite where people were observation Television set was far lower — 50 lx or less in 8 out of every 10 rooms measured, and below 13 lux for one-third of the suite.
Indoor light only may not provide enough buoyant to trammel inappropriate eyeball growth.
The eye is also in a Thomas More relaxed position outdoors, says Andy Fischer. He's a life scientist at Ohio State University who studies the retina. That eye relaxation whitethorn close off growth signals, too, he says.
And compared with indoor viewing, outdoor exposures provide a different set of peripheral images, those seen out of the corner of the centre. And even peripheral images can be in operating room out of focus. Indoors, thither's a mix of focused and unfocused images coming from the periphery, as whatever glimpse about a nipper's bedroom will show, says Frank Schaeffel of Tubingen University in Germany. At that place are cabinets, a door farther away, a computer screen up encompassing, you name it.
Being outdoors offers a field of vision that's Sir Thomas More unvarying. It's unmatchable that's also Thomas More like our prehistoric ancestors' view of the world. Throughout evolution, Fischer says, humans worn-out almost wholly their time outside. As a result, our eyes evolved to befit that environment. New behaviors — equal living in an industrialized high society and disbursal more metre in classrooms — place unnatural demands connected the eyes. These indoor behaviors may non mesh well with world' antediluvian genetic programming, he says.
Same with near work. Our Stone Age ancestors didn't read. Even those who chipped arrow points or did other fine work probably didn't do it all day, every Clarence Day. Constant just about bring off arrived only with culture.
Past work by Saw at the National University of Singapore and others has linked less outdoor exposure and more than near work to nearsightedness. "Reading, piece of writing and computer work contribute to shortsightedness," Power saw says. "We found that children who on a regular basis spend time on computers have a higher take a chanc."
And so shortsightedness might atomic number 4 nourished by a combination of too much near solve and too little outdoor exposure. After each, mortal who reads much in all likelihood does it inside; same with watching television or unmoving at a computer.
Saturation point
Some scientists have seen decent. "We need to get the message out to parents," says William Stell of the University of Calgary, in Canada. "Kick the kids outside."
Ian J. P. Morgan agrees, just says it won't represent easy in some places. In Chinese schools, for example, children nap indoors for an hour or two at lunchtime. The idea is to rent them respite up so that they can address through hours of homework later.

And it mightiness be hard to interchange this routine, he says. "When I floated the idea of fillet naps at lunchtime in China, the response was almost like I was advocating tyke cruelty," Morgan says. Kids in North United States of America and Europe may work hard, he says, "but you personal't seen nothing until you've seen China."
Yet, getting children outdoors might be easier than cutting spinal column on near work, Saw says. The Asian educational system has reached a "saturation full stop" of intensity level and competition, she says, simply no one wants to tell children to read or workplace less.
In the United States, middle doctors are becoming aware of the outdoor-exposure theory. But many a father't see a child until after the kid has unsuccessful an eye exam at school, says psychologist Jane Gwiazda of the New England College of Optometry. That may be too late. "Once a child is nearsighted," she says, "sending them outdoors to play may non barricade the cognitive operation."
Short-dated of getting out, maybe gazing out would help. It didn't seem to damaged baseball histrion Hornsby. Asked once what he did all wintertime during the off-season, he snapped: "I'll tell you what I coif. I gaze out the windowpane and wait for bounce."
Business leader Wrangle
20/20 vision This is the clarity of focus for images 20 feet outside that are typical for people with healthy, whole visual modality. Someone World Health Organization instead has 20/100 vision sees only too at 20 feet as masses with normal vision would see at 100 feet, or five times farther out.
cataract A vision impairment caused by a cloudiness in a membrane that covers the lense of the eye. Unremedied, IT can lead to blindness.
epidemiologist Like health detectives, these researchers puzzle out what causes a particular illness you bet to limit its spread.
glaucoma Eye disease that is the equivalent of hypertension: the pressure exerted past fluid privileged the eye becomes excessively high. That pressure sensation can damage the nerve carrying vision signals — and, if untreated, lead to partial operating theater total blindness.
lux A measurement unit for the story of light.
myopia The medical condition for nearsightedness.
myopic An unfitness to concenter anything that isn't nearby. Information technology's imputable an elongation of the eyeball. Many factors can contribute to this inappropriate elongation, and so the cause of nearsightedness is still under debate.
neurobiologist Scientist who studies cells and functions of the brain and other parts of the nervous system.
oculist In the United States, this is someone trained and authorized to examine eyes for defects and to prescribe treatment operating theatre restorative lenses. Although eye doctors, optometrists are not trained as physicians. Physicians World Health Organization narrow in the eye are called ophthalmologists.
retina A level at the back of the eyeball containing cells that are sensitive to light and that trigger nerve impulses that follow the optic tract to the brain, where a visual percept is formed.
Word See (click hither to print puzzle)

0 Response to "Fuzzy future"
Postar um comentário